In electronics manufacturing, ensuring product quality and reliability is a top priority.
As technology advances and electronic devices become smaller and more
sophisticated, they also become more vulnerable to even the tiniest electrical
disturbances. One such disturbance, known as electrostatic discharge (ESD), can
wreak havoc on sensitive electronic components, leading to costly failures and
compromised functionality. This is why stringent ESD protection protocols are an
absolute must in the electronics manufacturing industry.
Electrostatic discharge occurs when there is a sudden transfer of static electricity
between two objects with differing electrical potentials. In everyday life, ESD is the
shock you might feel when touching a doorknob after walking on carpet. However, in the context of electronics, ESD can have far more damaging consequences. Even a seemingly harmless discharge, one that is imperceptible to humans, can destroy or degrade delicate electronic components.
Semiconductor devices, microchips, and other intricate parts are particularly
susceptible to ESD. These components operate at extremely low voltages, meaning
even a small static discharge can disrupt their functionality. When ESD damages a
component, the effects can range from immediate failure to latent damage, which
may not manifest until the device is in use, leading to costly repairs or recalls down
the line.
Why ESD Protection is Essential
● Preventing Damage to Sensitive Components: As electronic devices shrink in
size, the internal components also become more compact and complex. The
smaller the component, the more vulnerable it is to static discharge. Without
adequate ESD protection, manufacturers run the risk of introducing defects
into their products right from the production line. Damage caused by ESD may
not always be visible to the naked eye, making it even more critical to
safeguard these parts during the entire manufacturing process.
● Maintaining Product Quality and Reliability: In the electronics industry,
maintaining high standards of quality is non-negotiable. A single faulty device
can lead to customer dissatisfaction, damage a company's reputation, and
even result in significant financial losses. By implementing strict ESD control
measures, manufacturers can reduce the likelihood of defects and ensure
their products meet rigorous quality standards.
Additionally, many industries that rely on electronic devices, such as aerospace,
medical, and automotive sectors, have no tolerance for device failures. ESD
protection helps guarantee that electronic components used in these critical
applications function reliably over time.
● Minimizing Costs and Waste: One of the most tangible benefits of ESD
protection is cost savings. When ESD-related failures occur, the manufacturer
may need to rework or scrap entire batches of products, leading to increased
production costs and material waste. Effective ESD control helps prevent
these failures, allowing companies to maintain efficient production processes
and minimize unnecessary expenses.
Moreover, the cost of implementing ESD protection measures is relatively low
compared to the potential financial impact of an ESD event. Investing in proper
grounding systems, antistatic materials, and employee training can save companies
from the much higher costs associated with product recalls, warranty claims, and
damaged customer trust.
ESD protection is not just a good practice; it's often a legal and industry requirement.
Various international standards, such as the ANSI/ESD S20.20 and IEC 61340-5-1,
outline best practices for controlling ESD in manufacturing environments. These
standards provide guidelines for establishing an effective ESD control program,
including the use of protective clothing, wrist straps, grounding equipment, and
controlled environments.
Compliance with these standards is necessary for manufacturers to remain
competitive in the global market. Failing to meet ESD control requirements can result in lost business opportunities and restricted access to certain markets, particularly in industries that demand the highest levels of reliability and safety.
To combat the risks associated with electrostatic discharge, manufacturers
implement a variety of protective measures throughout the production process.
Some of these include:
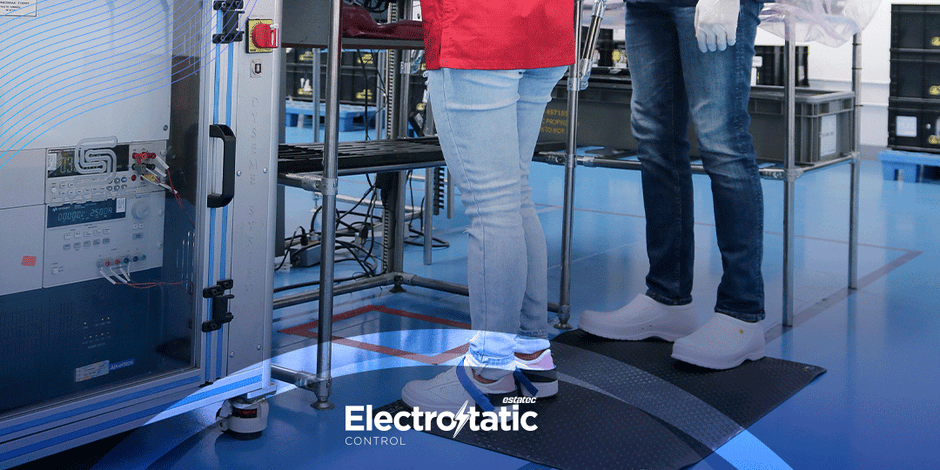
● Grounding Systems: All tools, workstations, and employees must be
grounded to ensure that static electricity is safely dissipated.
● Antistatic Materials: ESD-safe mats, packaging materials, and clothing are
used to prevent the buildup of static charges.
● Humidity Control: Maintaining an appropriate level of humidity in the
manufacturing environment helps reduce static electricity.
● Employee Training: Workers must be trained on proper ESD handling
techniques to minimize the risk of unintentional damage to sensitive
components.
● Controlled Access Areas: Establishing ESD-controlled workstations or rooms,
where static-generating materials are prohibited, adds an extra layer of
protection for vulnerable components.