Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a significant challenge in industries dealing with
sensitive electronic components. To mitigate the risks posed by static electricity,
specialized workspaces called ESD workstations are essential. These workstations
are designed to prevent the build-up and transfer of static electricity, safeguarding
delicate equipment and ensuring smooth operations. In this article, we'll explore the various types of ESD workstations and their core components.
Types of ESD Workstations
1. Basic ESD Workstations: A basic ESD workstation offers essential protection
against static build-up. It typically consists of an ESD-safe work surface, grounding
points, and wrist straps. These are most commonly found in environments where
static-sensitive components are handled sporadically, but where overall protection is still required. The simplicity of these workstations makes them cost-effective and
easy to maintain.
2. Modular ESD Workstations: Modular ESD workstations are versatile and
customizable. They allow users to configure their setup based on specific
requirements, such as additional shelving, lighting, or tools. These workstations are
often used in industries that require flexibility, such as electronics assembly or repair.
Modular designs make it easier to add or remove components as needs evolve,
making them a long-term solution for dynamic work environments.
3. Full ESD Workbenches: For high-volume production facilities or research labs, full
ESD workbenches are a more robust solution. These workbenches are fully
equipped with ESD-safe mats, chairs, racks, and grounding systems. They offer
greater workspace and more comprehensive static protection, suitable for
continuous handling of static-sensitive components. Full ESD workbenches are also ergonomically designed, enhancing comfort and reducing strain during extended work periods.
Key Components of ESD Workstations
No matter the type, ESD workstations rely on certain key components to function
effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the essential elements:
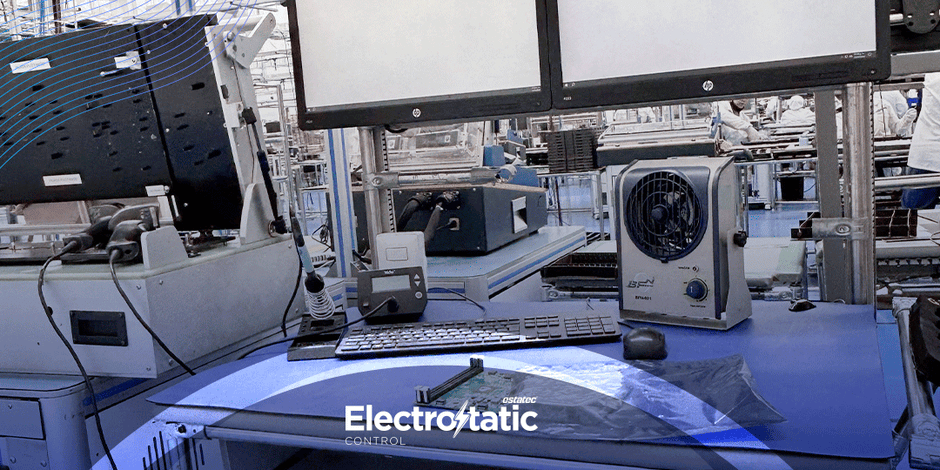
1. ESD-Safe Work Surface: The work surface is one of the most critical parts of any
ESD workstation. Typically, it’s made of static-dissipative materials like rubber or
vinyl, designed to safely channel any static charges away from sensitive electronics.
The surface is usually connected to a grounding point, ensuring that any electrostatic charges are neutralized. Proper cleaning and maintenance are essential to keep the surface functioning efficiently, as dust or debris can impact its effectiveness.
2. Grounding Points: Grounding is the backbone of an ESD-safe environment.
Grounding points are placed at key locations on the workstation, connecting to the
work surface, wrist straps, and any tools that might accumulate static charge. By
grounding these components, static electricity can safely dissipate without posing a
threat to electronic devices. Ensuring that all components are properly grounded is
vital for maintaining a secure workstation.
3. Wrist Straps: Wrist straps are perhaps the most recognizable component of ESD
workstations. These straps are worn by operators to ensure that any static charge
their body might generate is safely discharged. Connected to the workstation’s
grounding system, wrist straps are adjustable and designed for comfort during long
shifts. For environments where mobility is required, wireless or cordless wrist straps
are available, offering freedom of movement without compromising safety.
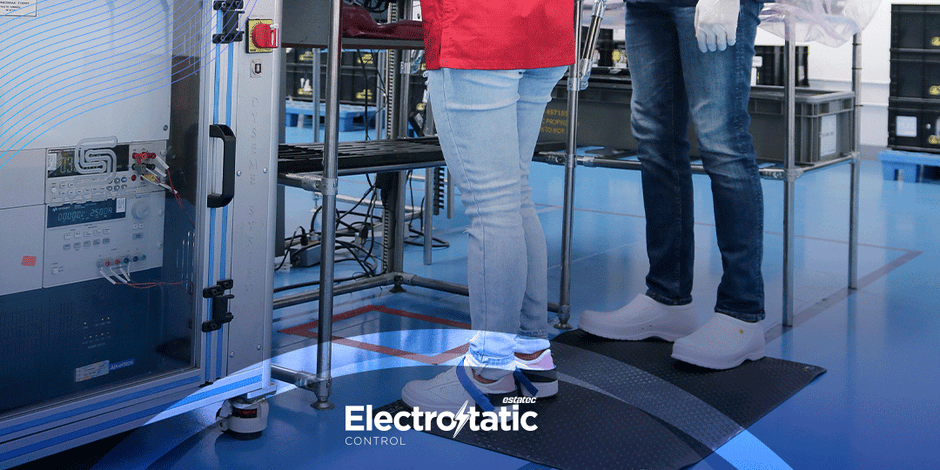
4. ESD-Safe Mats: In addition to the work surface, ESD-safe mats are often placed
on the floor around the workstation. These mats ensure that any static charge
generated by movement or foot traffic is dissipated before it can reach the work area.
ESD mats come in various sizes and materials, often made from durable vinyl or
rubber to ensure longevity. These mats also help reduce fatigue, providing a
comfortable surface for operators to stand on during long work periods.
5. ESD-Safe Tools and Equipment: Handling sensitive components requires the use
of tools that won’t generate or transfer static electricity. ESD-safe tools are specially
designed with static-dissipative materials, ensuring that any charge they accumulate is safely transferred to the ground. These tools include screwdrivers, pliers, tweezers, and soldering irons, all of which play an integral role in ensuring static-free assembly or repair work.
6. Ionizers: In certain environments, grounding alone may not be sufficient to
eliminate static charge, especially in dry or dust-prone areas. Ionizers are devices
that neutralize static electricity by emitting charged particles into the air. By balancing the ionization in the environment, they help to prevent static build-up on surfaces, tools, or components. Ionizers are particularly useful in cleanrooms or laboratories where maintaining an ESD-safe environment is critical.
7. ESD-Safe Storage: Finally, static protection doesn’t stop at the workstation. ESD-safe storage solutions, such as bins, racks, and cabinets, are essential for keeping components safe when not in use. These storage units are made from conductive or static-dissipative materials and are grounded to prevent the build-up of static charge.
Proper storage is vital for maintaining the integrity of sensitive electronic parts
throughout the production process.