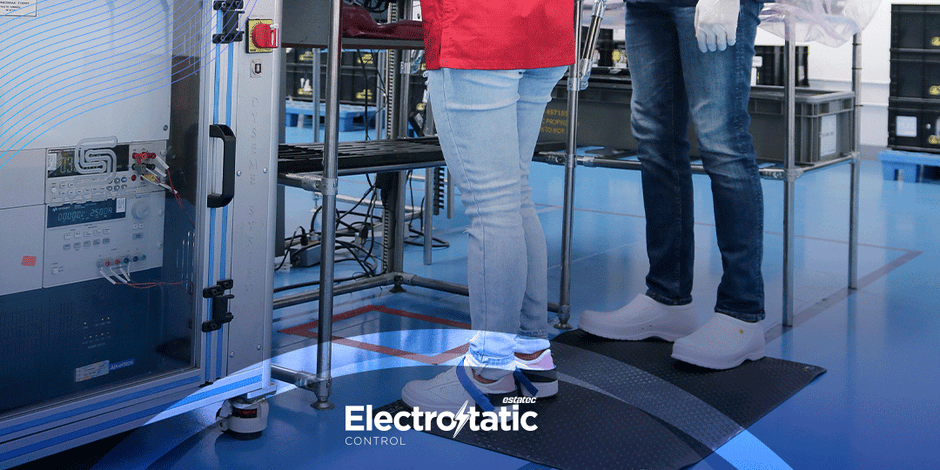
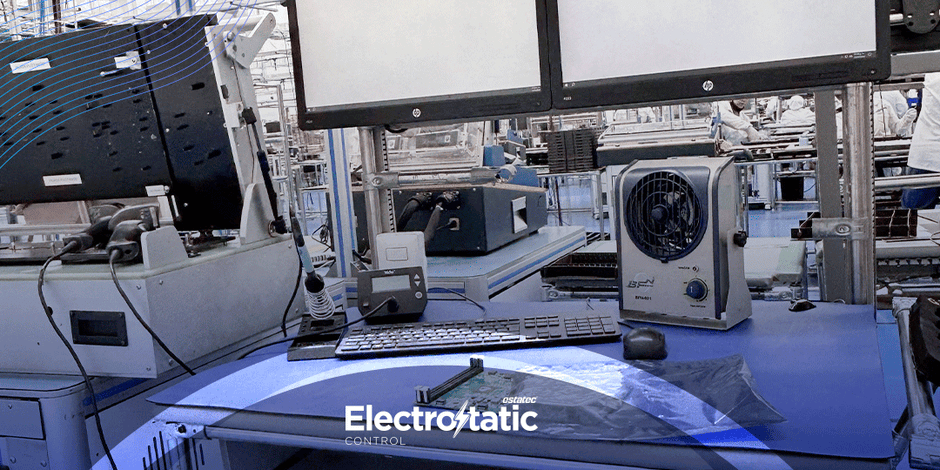
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a silent threat in electronics manufacturing that
can lead to significant failures if not effectively managed. Here are real-world
examples of ESD-related failures, what went wrong, and the critical lessons
learned to prevent future incidents.
1. Catastrophic Failure in Semiconductor Manufacturing.
Incident:
A semiconductor manufacturing facility experienced a massive failure rate in their production line. Over 20% of their integrated circuits were failing final tests,
resulting in substantial financial losses and delays in product delivery.
What Went Wrong:
The root cause was traced back to improper handling of components by operators
who were not using ESD-safe practices. Wrist straps were either not worn or not
properly grounded, and workstations lacked adequate ESD protection.
Lesson Learned:
Implement stringent ESD training programs for all employees. Ensure that personal
grounding devices are used consistently, and workstations are equipped with
proper ESD controls. Regularly audit and test ESD safety measures to ensure
compliance.
2. Medical Device Malfunctions.
Incident:
A medical device company faced a recall of thousands of units after reports of
malfunctions in the field. These devices, used in critical care settings, were failing
sporadically, putting patient safety at risk.
What Went Wrong:
Investigations revealed that ESD during the assembly process caused latent
defects in sensitive electronic components. The assembly line lacked
comprehensive ESD controls, and operators were unaware of ESD risks.
Lesson Learned:
Adopt a robust ESD control program throughout the manufacturing process. Use
ESD-safe materials and equipment and ensure that all personnel understand the
importance of ESD prevention, particularly in industries where device reliability is
critical.
3. Aerospace Component Failures.
Incident:
An aerospace manufacturer encountered unexpected failures in avionic
components, leading to costly repairs and replacements. These failures were
particularly concerning given the critical nature of aerospace applications.
What Went Wrong:
The failures were attributed to ESD damage during the assembly of printed circuit
boards (PCBs). The company’s ESD control measures were outdated and
insufficient for handling the increasingly sensitive components.
Lesson Learned:
Update ESD control measures to keep pace with advancements in technology and
the increasing sensitivity of electronic components. Ensure that all assembly areas
are equipped with state-of-the-art ESD protection and that employees are trained
on the latest ESD prevention techniques.
These real-world examples highlight the severe consequences of ESD failures in
various industries. The lessons learned emphasize the importance of
comprehensive ESD control programs, regular training, and the use of appropriate
ESD-safe materials and equipment. By adopting these practices, companies can
protect their products, reputation, and bottom line from the hidden dangers of
electrostatic discharge.