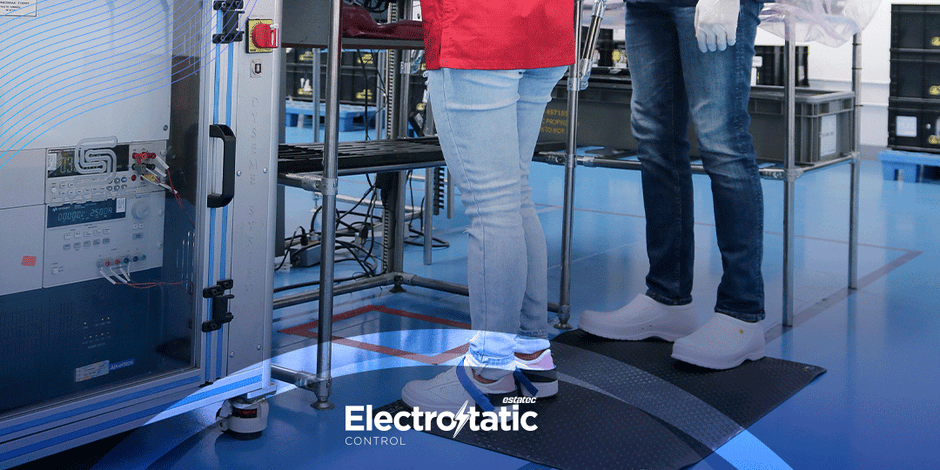
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can wreak havoc on sensitive electronic components,
causing irreparable damage and costly failures. ESD mats are a crucial tool in
mitigating these risks by grounding static electricity. However, to maximize their
effectiveness, proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting are essential.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to mastering electrostatic control with ESD mats.
ESD mats are designed to dissipate static electricity, grounding any charged
particles and preventing static buildup that could potentially damage electronic
devices. They are typically made from conductive or dissipative materials and come
in various forms, including table mats, floor mats, and runners. Their primary function is to create a controlled environment that minimizes the risk of electrostatic
discharge.
Installation Tips for ESD Mats
1. Choose the Right Mat: Selecting the appropriate ESD mat for your workspace is
the first step. Consider the type of work being done and the environment. For
instance, anti-fatigue ESD floor mats are suitable for areas where employees stand
for long periods, while ESD table mats are ideal for workbenches handling sensitive
electronics.
2. Proper Grounding: Ensure that the ESD mat is properly grounded. This typically
involves connecting the mat to a grounded point using a grounding cord. A common practice is to use a ground snap installed on the mat, which then connects to a grounding plug or direct ground point. Always verify the integrity of the ground connection using a continuity tester.
3. Clean, Flat Surface: Install the ESD mat on a clean, flat surface free of debris. Any bumps or dirt underneath the mat can interfere with its performance. Cleaning the surface beforehand ensures optimal contact between the mat and the ground.
4. Positioning: Place the ESD mat in areas where static-sensitive work is performed.
For table mats, ensure they cover the entire work surface. For floor mats, position
them in high-traffic areas where personnel frequently move, such as near
workbenches or assembly lines.
Maintenance Techniques
1. Regular Cleaning: Keep the ESD mats clean to maintain their effectiveness. Use a mild, ESD-safe cleaner and a soft cloth or mop to wipe down the mats. Avoid harsh chemicals that can degrade the mat’s material. Regular cleaning prevents the
accumulation of dust and other contaminants that can interfere with static
dissipation.
2. Inspect Grounding Connections: Periodically check the grounding connections to
ensure they remain secure. Loose or corroded connections can compromise the
mat’s ability to effectively dissipate static electricity. Tighten any loose connections
and replace corroded components as needed.
3. Monitor Wear and Tear: Over time, ESD mats can wear down, especially in high-
traffic areas. Inspect the mats regularly for signs of wear such as cuts, tears, or
discoloration. Replace mats that show significant wear to ensure continuous
protection against ESD.
4. Use ESD-Safe Accessories: Ensure that all accessories and tools used in
conjunction with the ESD mat are also ESD-safe. This includes wrist straps,
footwear, and other personal grounding equipment. Using incompatible accessories
can reduce the effectiveness of the ESD mat.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. Ineffective Grounding: If you notice that static discharge events are still occurring, check the grounding system. Ensure that the grounding cord is intact and securely connected to a proper ground point. Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the ground connection, which should be less than 1 ohm.
2. Mat Slippage: If the ESD mat is slipping or moving out of place, use non-slip tape
or adhesive to secure it to the floor or workbench. Some mats come with a non-slip
backing, but additional securing measures can provide extra stability.
3. Contaminant Build-Up: In environments with high dust or chemical exposure, ESD mats can become contaminated, reducing their effectiveness. Implement a more frequent cleaning schedule and consider using protective covers that can be easily cleaned or replaced.
4. Static on Personnel: If personnel continue to experience static shocks, ensure
they are properly grounded with wrist straps or ESD-safe footwear. Additionally,
verify that the humidity levels in the workspace are within the recommended range
(40-60%) as low humidity can increase static buildup.
Effectively using ESD mats involves more than just placing them in the workspace.
Proper installation, regular maintenance, and vigilant troubleshooting are crucial to
ensuring these mats perform their role in preventing electrostatic discharge. By
following these guidelines, you can create a safer, more reliable environment for
handling sensitive electronic components. Remember, the goal is to master
electrostatic control, and with these essential tips, you are well on your way to
achieving that mastery.