Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden flow of electricity between two
electrically charged objects caused by contact, an electrical short, or dielectric
breakdown. While often imperceptible to humans, ESD can have significant and
sometimes catastrophic effects on electronic devices and components.
Understanding the science behind ESD, its causes, and its effects on electronics is
necessary for implementing effective ESD protection measures.
ESD occurs when accumulated static electricity is released suddenly. This buildup
of static electricity can happen through various means, such as friction (triboelectric
charging), induction, or conduction. When two materials come into contact and
then separate, electrons can transfer from one material to the other, creating an
imbalance of charges. This imbalance creates an electric field. When the difference
in electric potential between two objects becomes sufficiently large, it can cause a
rapid discharge of electrons, known as ESD.
Causes of ESD.
1.Triboelectric Charging: The most common cause of ESD is triboelectric charging,
which occurs when two materials rub together and then separate. This can happen
with everyday actions like walking on a carpet, handling plastic bags, or working
with certain textiles.
2.Induction: ESD can also be caused by induction, where an electrically charged
object is brought near a conductive object, inducing a charge without direct
contact.
3.Conduction: Direct contact between objects with different electric potentials can
result in an ESD event. This can occur when a person touches an electronic
component without proper grounding.
Effects of ESD on Electronics.
ESD can have a range of detrimental effects on electronic components and
systems:
1.Immediate Damage: ESD can cause immediate and permanent damage to
electronic components, such as semiconductor devices, by creating electrical
shorts or damaging delicate internal structures.
2.Latent Damage: ESD may cause latent defects that do not immediately result in
component failure but can lead to reduced performance or reliability over time.
These latent failures are often difficult to detect and can lead to unexpected system
failures in the future.
3.Data Corruption: ESD events can also cause data corruption in memory devices
and disrupt the operation of microprocessors, leading to system crashes and data
loss.
Why ESD Protection is Critical.
Given the potential for severe damage, implementing ESD protection is critical in
environments where sensitive electronic components are handled or
manufactured. Effective ESD protection measures include:
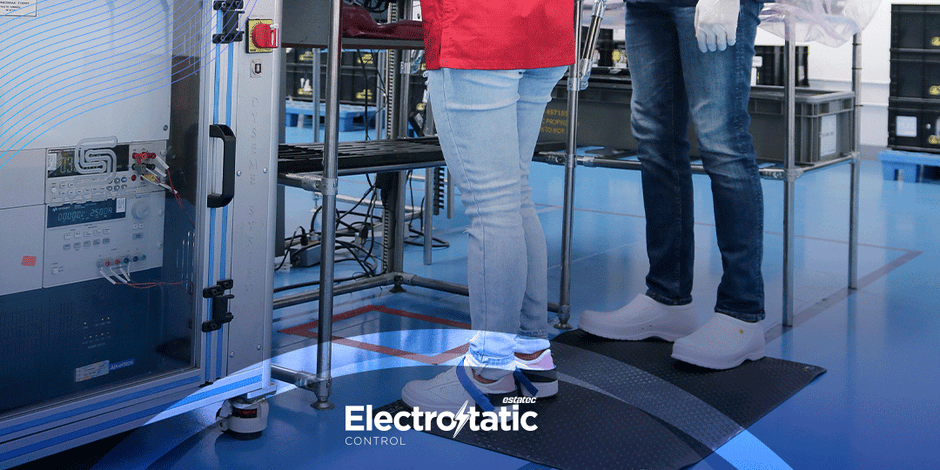
1.Grounding and Bonding: Ensuring that all conductive materials and personnel
are properly grounded to dissipate static charges safely.
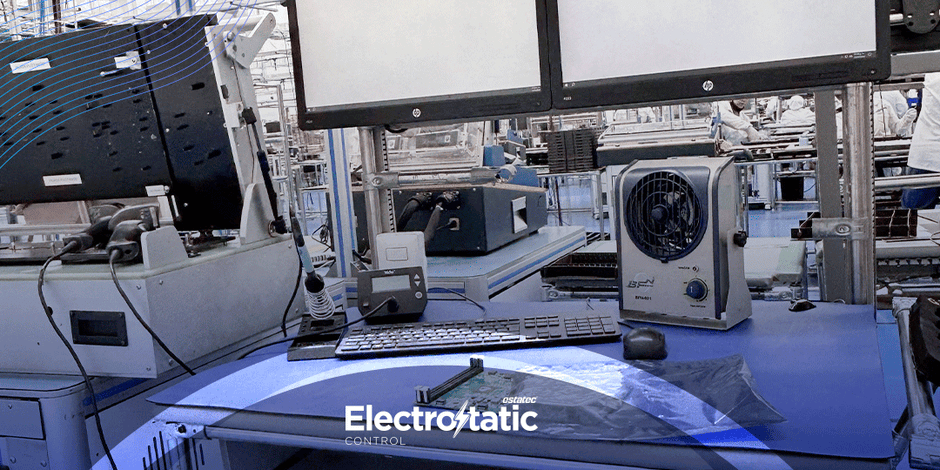
2.ESD-Safe Workstations: Using ESD-safe workstations equipped with grounded mats, wrist straps, and other protective equipment to prevent static buildup.
3.Antistatic Materials: Utilizing antistatic bags, containers, and packaging materials
to protect components during storage and transportation.
4.Environmental Controls: Maintaining controlled humidity levels to reduce static
buildup and using ionizers to neutralize static charges in the air.
5.ESD Training: Educating personnel on proper ESD handling procedures and the
importance of following ESD protection protocols.
By implementing comprehensive ESD protection measures, manufacturers and
technicians can safeguard electronic devices, ensuring their reliability and
longevity. ESD protection is not just a technical requirement but a critical aspect of
maintaining the integrity and performance of modern electronic systems.